CCTA scenario
Background: Addressing Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) early is crucial for reducing heart disease’s global impact. The demand for non-invasive, cost-effective diagnostic tools is rising, driven by the need to minimize patient risk and healthcare costs.
Problems: Traditional CAD diagnostics, often invasive and reliant on contrast agents, present safety and cost concerns. There’s a critical need for innovative methods that leverage patient data without these drawbacks.
Objectives: Develop an AI-powered, non-invasive diagnostic application that:
- Analyzes lab reports, calcium scoring, and epicardial fat volume to predict obstructive CAD risk.
- Offers a safer, cost-effective alternative to contrast-enhanced CCTA.
- Supports early intervention with accurate, timely risk assessment.
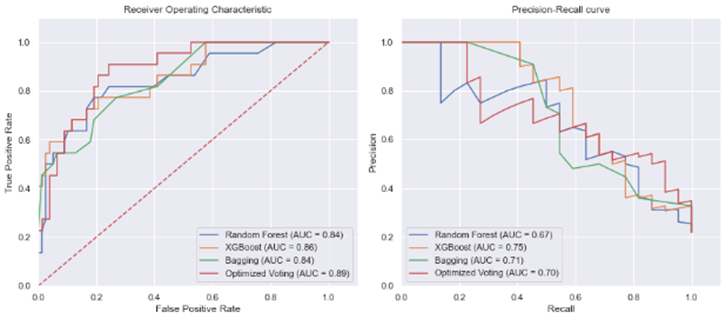
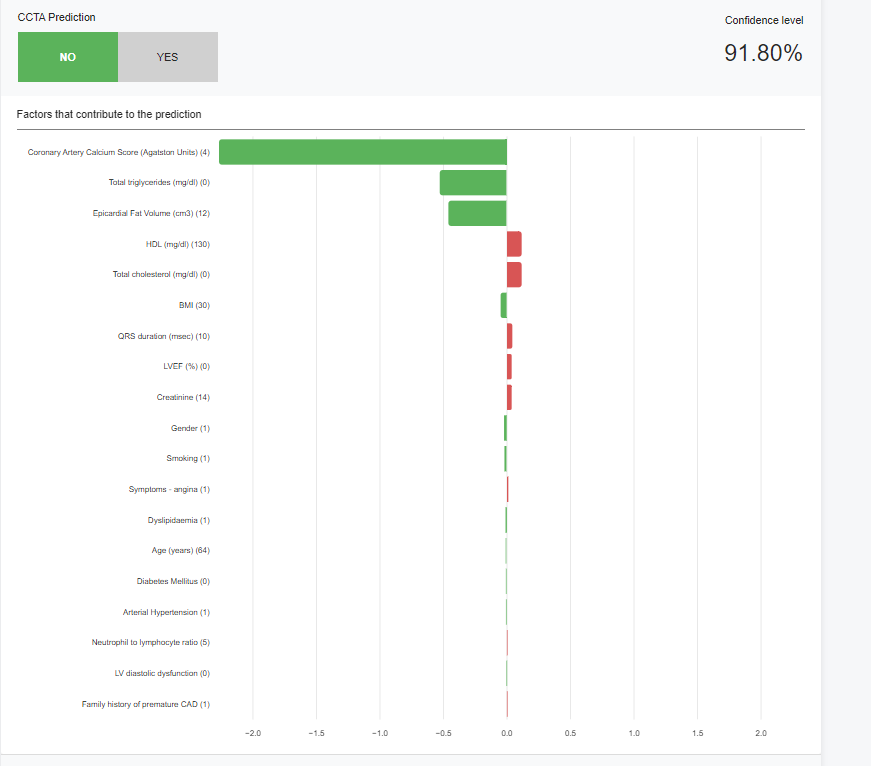
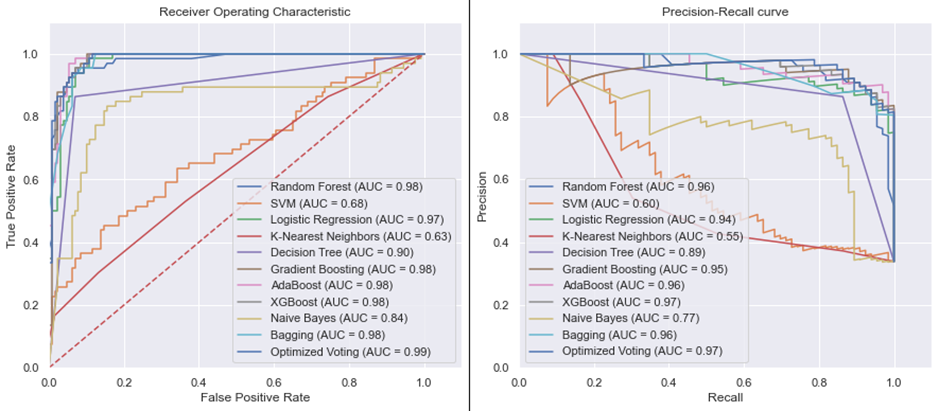
The Solution: An AI application utilizing machine learning to predict CAD from non-contrast data, including laboratory findings and imaging results. It aims for high accuracy without immediate CCTA use, prioritizing patient safety and reducing costs.
SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) enhance model interpretability, giving clinicians insight into predictions.